
the applications of stem cells, a major advance in the field of regenerative medicine. Find out how stem cells are being used to treat different medical conditions and the exciting prospects for the future.
Stem cells details
Stem cells
Prices
About
Definition
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells (unique homogeneous cells) present in the human body that have the ability to differentiate into different types of specialized cells. They are essential for tissue growth, repair and regeneration. Stem cells can develop into cells that serve numerous functions in different body parts during early life and growth. Thanks to their potential for differentiation, stem cells offer many promising therapeutic applications.
Stem cells, in many tissues, can act as an internal repair system, dividing essentially without limit to replenish other cells, regenerate and replace damaged tissues and organs in the body.
Stem cells can treat many diseases, for example, diabetes type 1, dementia, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and rheumatoid arthritis, injuries and genetic disorders. Scientific research reveals that human Amniotic Fluid Mesenchymal Stem Cells (hAF-MSCs) are highly effective. Not only in the rejuvenation of the body but also in repairing accident or age- related tissue damage.
This exciting, cutting edge medical treatment is evolving rapidly.
The Different Types of Stem Cells
There are 3 types of stem cells
1. Embryonic Stem Cells
Embryo stem cells are extracted from human embryos and are capable of differentiating into all types of cells in the human body. They are used in the research and development of treatments for many diseases.
2. Adult Stem Cells
Adult stem cells are found in different tissues of the body, such as bone marrow, blood, skin, and fatty tissue. They are responsible for the regeneration and repair of damaged tissues.
3. Induced Stem Cells
Induced stem cells, also known as iPS cells, are adult cells reprogrammed in the laboratory to acquire characteristics similar to those of embryonic stem cells. They offer an ethical alternative to embryonic stem cells for research and therapeutic applications.
Characteristics of stem cells
Cells that have the potential to transform into different types of cells and renew themselves are called "stem cells". Stem cells have two important characteristics: First, these cells can divide to renew themselves over long periods of time, millions of cells can arise from a single stem cell.Second, a stem cell cannot work with its neighbors to pump blood throughout the body, such as in heart muscle, cannot transport oxygen to tissues such as red blood cells, or transmit signals electrochemicals needed by tissues and organs such as nerve cells. However, unspecialized stem cells can come from specialized cells such as heart muscle cells, blood cells, or nerve cells.
Four basic characteristics of stem cells are very important in the use of these cells for therapeutic purposes:
- They can settle in the area of inflammation when they are injected into the vein after tissue damage
- They can secrete a large number of bioactive molecules that allow damaged cells to heal and suppress inflammation
- They do not cause of allergic reactions in the body and have functions of regulating the immune system
- They differentiate into different types of cells
Although stem cells are theoretically obtained from many tissues and organs, at present the most widely used sources in stem cell applications for therapeutic purposes are; bone marrow, umbilical cord and amniotic fluid, joint fluid or membrane and umbilical fatty tissue.
Therapeutic Applications of Stem Cells
Stem cells are used in the treatment of various diseases and medical conditions. Here are some examples of therapeutic applications of stem cells:
- Regeneration of muscle and bone tissue
- Treatment of heart disease
- Repair of spinal cord injuries
- Gene therapy for genetic diseases
- Treatment of neurodegenerative diseases
Today the few specialized clinics and hospitals offer already defined treatments for perfectly identified pathologies on a wide spectrum ranging from autism, Crohn's disease, to multiple sclerosis as well as the extension of treatments for rejuvenation.
In orthopedics, plastic surgery and dermatology, stem cell applications are replicated around the world and show spectacular clinical results.
For some stem cell applications, local anesthesia may be used, but most stem cell applications do not require anesthesia.
Injection of stem cells and cellular tissue engineering
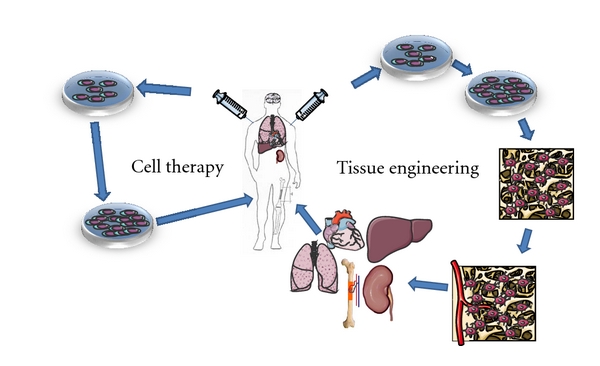
Application Policy Schema
Application strategies
There are two main strategies for the application of stem cells in regenerative medicine. Stem cells can be taken either from the patient himself (autologous transplant) or from donors (allogeneic transplant). These cells are then multiplied in the laboratory (in vitro) and used in two different ways.
1. The first method, called "cell therapy", involves applying stem cells directly to the patient to replace lost or damaged cells. Stem cells can differentiate into different cell types depending on the treatment needs.
2. The second method, called "tissue engineering", involves seeding the stem cells into three-dimensional scaffolds. These scaffolds provide structural support to cells and allow their differentiation into a specific cell type. Once the composite artificial tissue is constructed, it is then implanted in the area where the patient's tissue is damaged.
These approaches aim to regenerate tissues and restore their function in the body, thereby providing new treatment possibilities for various diseases and injuries.
Photo credit: TY - DAY AU - Schmitt, Andreas AU - van Griensven, Martijn AU - Imhoff, Andreas B. AU - Buchmann, Stefan Y - 2012/02/23 SP-394962 T1 - Application of Stem Cells in Orthopedics VL - 2012 DO - 10.1155/2012/394962 OJ - Stem cells international ER -
Future Prospects of Stem Cells
Stem cell research opens up many exciting possibilities for the future. Scientists are exploring new therapeutic applications, such as therapeutic cloning, tissue engineering and advanced regenerative medicine. These advances could potentially revolutionize the treatment of many diseases and medical conditions.
Risks
Despite their promising potential, the use of stem cells also carries risks. Some of the potential risks include:
- Tumor formation
- Graft rejection
- Ethical and legal issues related to the use of embryonic stem cells
Today the few specialized clinics and hospitals offer already defined treatments for perfectly identified pathologies on a wide spectrum ranging from autism, Crohn's disease, to multiple sclerosis as well as enlargement of treatments for rejuvenation.
In orthopedics, plastic surgery and dermatology, stem cell applications are replicated around the world and show spectacular clinical results.
The competent authorities, the Turkish Ministry of Health have already approved cell treatments for the following pathologies:
- Covid-19 pneumonia
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF)
- Chronic pulmonary obstruction
- Disease (COPD)
- Diabetic Foot Injuries
- Peripheral arterial disease
- Spinal cord injury
- Cerebral palsy (CP)
- Head Injury (TBI)
- Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE)
- Spinocerebellar Ataxia (SCA)
- Friedreich's Ataxia (FA)
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD)
- Cystic Fibrosis (CF)
- Treatment of ischemic heart disease
- Autoimmune encephalitis (AE)
- Miyoshi Myopathy Limbs Belt
- Muscular Dystrophy (LGMD)
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Stroke
- Congenital progressive myopathy
- Optic atrophy
- Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP)
- Erectile dysfunction
- Ovarian failure
- Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis)
- Crohn's disease
- short bowel syndrome
FAQ
A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell capable of differentiating into different types of specialized cells in the body.
There are three main types of stem cells: embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells and induced stem cells.
Stem cells are used in the treatment of a variety of diseases and medical conditions, including tissue regeneration, treatment of heart disease, repair of spinal cord injury, gene therapy, and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.< /p>
Stem cells open up many exciting avenues for the future, such as therapeutic cloning, tissue engineering and advanced regenerative medicine.
Potential risks of using stem cells include tumor formation, graft rejection, and ethical and legal issues related to the use of embryonic stem cells.
Les cellules souches peuvent être trouvées dans divers tissus du corps, tels que la moelle osseuse, le sang, la peau et les tissus adipeux.
Yes, stem cells are widely used in scientific research to better understand cell development, study diseases and develop new therapies.
Challenges include the safety and efficacy of stem cell-based treatments, as well as ethical and regulatory issues surrounding their use.
Yes, it is possible to preserve your own stem cells, in particular through the preservation of umbilical cord blood or the cryopreservation of adipose tissue.
Stem cells play a key role in regenerative medicine by enabling the repair and regeneration of damaged or diseased tissues in the body.
Embryonic stem cells come from state approved stem cells banks.
NAD+ Intravenous Therapy
Prices
About
Introduction to NAD+ Intravenous Therapy
NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide), a pivotal coenzyme present in all living cells, plays a crucial role in the fundamental biological processes of our body. Essential for mitochondrial function, NAD+ is instrumental in converting nutrients into ATP, the energy currency of our cells. This process not only fuels cellular activities but also regulates DNA repair and contributes to the lengthening of telomeres, associated with aging.
Beyond its critical function in energy metabolism, NAD+ exerts a remarkable influence on overall well-being. Its benefits extend to enhancing skin health, giving it a youthful and vibrant appearance. In the cardiovascular realm, NAD+ supports heart health and functionality. Its impact on the neurological system is profound, affecting neurotransmitter levels, which in turn enhances cognitive functions like concentration and memory, and stabilizes mood.
Moreover, NAD+ plays a significant role in bolstering the immune system, fortifying the body's natural defenses. The comprehensive benefits of NAD+ intravenous therapy make it a sought-after treatment for those looking to optimize their health and vitality, offering a pathway to improved wellness and quality of life.
FAQ
Stem cells - Rejuvenation packages
Prices
About
Facial Rejuvenation with Stem Cell Therapy
Facial rejuvenation through stem cell therapy is a groundbreaking approach in the field of aesthetic medicine, offering a natural and innovative way to enhance skin vitality and youthfulness. This therapy utilizes the regenerative capabilities of stem cells to repair and rejuvenate the skin at a cellular level.
Stem cells, known for their ability to regenerate and repair damaged tissues, are harnessed in this treatment to promote the growth of new skin cells, increase collagen production, and improve skin elasticity. This results in a more youthful appearance, with reduced fine lines and wrinkles, improved skin texture, and an overall enhancement in skin tone and firmness.
The treatment involves harvesting stem cells from a patient's own body - usually from areas like the abdomen or thighs - and then processing and reintroducing them to the facial area. This not only ensures a high level of safety and compatibility but also a more natural and long-lasting outcome compared to conventional anti-aging treatments.
Ideal for individuals seeking a non-invasive yet effective solution to combat signs of aging, stem cell facial rejuvenation stands as a cutting-edge option in the realm of cosmetic enhancements. It's a holistic approach that not only addresses aging symptoms but also promotes overall skin health.
FAQ
Stem Cell Hair Therapies
Prices
About
Stem Cell Therapies for hair
Stem cell therapies are opening a new chapter in the treatment of hair disorders, offering an innovative approach to combat hair loss and stimulate regrowth. These revolutionary treatments harness the regenerative power of stem cells to revitalize hair follicles and promote the growth of new hair.
By harvesting stem cells from the patient, specialists can reimplant them into balding areas, where they contribute to the regeneration of follicles and hair densification. This represents a natural and promising method for those looking for a non-invasive solution to hair loss.
With encouraging results, such as a significant increase in hair density and a reduction in hair fall, stem cell therapy for the scalp could well be the key to regaining a head full of healthy and vital hair.
FAQ
Stem Cells Regenerative Orthopedics
Prices
About
Stem Cell Use in Orthopedics
Regenerative orthopedics turns to stem cells to repair and rebuild damaged musculoskeletal tissues. This innovative approach offers to treat bone, cartilage, and muscle lesions by leveraging the body's innate healing potential.
Orthopedic stem cells, often harvested from the patient's own bone marrow or adipose tissue, are injected directly into the affected area to stimulate tissue regeneration and reduce inflammation, providing a promising alternative to traditional surgical interventions.
With their unique properties, stem cells represent a significant advancement in the treatment of joint pathologies, slow-healing fractures, and age-related degenerations, heralding the beginning of a new era in orthopedic medicine.
FAQ