
Regenerative medicine, The new hope of medicine available today!
"In truth, so far, modern medicine has not extended our natural lifespan by a single year. Its great achievement has been to save us from premature death and to allow us to fully enjoy our years. Even if we now overcome cancer, diabetes, and the other major causes of mortality, it would only mean that everyone could live up to ninety years - but this would entail reorganizing the most fundamental structures and processes of the human body and discovering how to regenerate organs and tissues."
- Yuval Noah Harari, HOMO DEUS
The hope generated by therapeutic advances based on stem cells precisely embodies the vision of the medicine of the future described by history professor Harari. Today, although increasing longevity is not yet a reality, improving quality of life has become a central topic in modern medicine. Living a long life implies living well, and it is here that the practical use of regenerative cellular therapies has been identified and is considered a leading therapeutic option in many countries.
What is Cellular Therapy?
Cellular therapy involves grafting cells to restore the activity of a tissue or organ, aiming to provide long-term healing for the patient through the injection of therapeutic cells.
Where Do the Used Cells Come From?
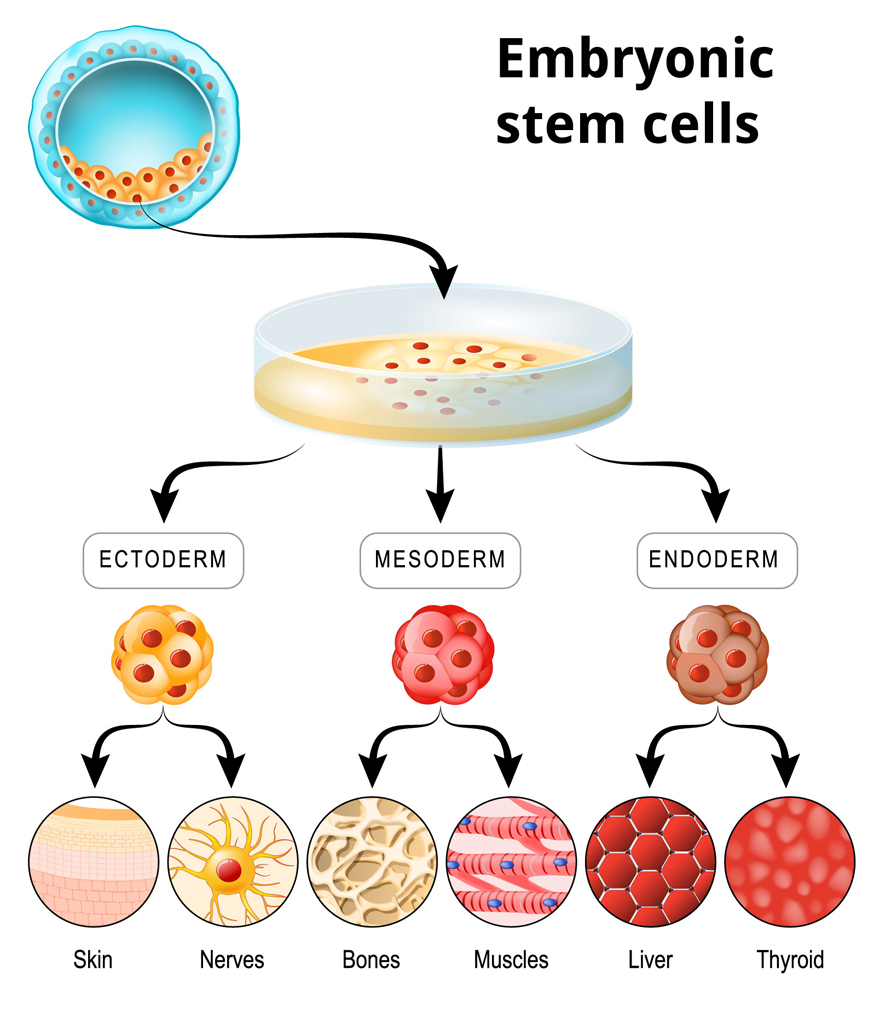
Stem cells, both embryonic and adult, have varied potentials. Embryonic stem cells, pluripotent, are found in early developmental stages and can differentiate into any cell type in the body. Adult stem cells, multipotent, are located in adult tissues and can transform into different types of cells, but only within their tissue of origin.
Properties of Stem Cells
Stem cells have the unique potential to transform into different types of cells and to renew themselves. They can divide and renew themselves over long periods and can originate from specialized cells.
Four key characteristics make them valuable for therapy:
- Their ability to settle in inflammation areas,
- To secrete bioactive molecules, which enable damaged cells to heal and suppress inflammation,
- To regulate the immune system without causing allergies,
- And to differentiate and replace into different types of cells.
Where are Stem Cells Obtained From?
The most common sources for obtaining stem cells in therapy are bone marrow, umbilical cord, joint fluids, and umbilical adipose tissue.
Some Types of Stem Cells
Adipose Tissue Stem Cells:
These cells, key in regenerative medicine, can migrate from their tissue of origin to the bloodstream, facilitating their collection for cellular therapies. It has recently been shown that mammalian adipose tissue can produce all of the cells that make up blood, particularly those of the innate immune system.
Embryonic Stem Cells (ESC):
These cells offer a renewable resource for studying and combating degenerative diseases, as well as for testing drugs and therapies.
Embryonic stem cells, especially mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord or amniotic fluid, are increasingly used in specialized clinics in Thailand, Colombia, and Turkey, where legislation is favorable to the use of stem cells as therapy.
These cells come from stem cell banks and are harvested directly in the country's hospitals. In Thailand and Colombia, legal advancements and medical infrastructure allow patients to benefit from treatments using these stem cells, which is not the case in some other countries where legislation is more restrictive. The cells can be used fresh or after undergoing a process of vitrification, a rapid freezing technique that allows preserving their biological properties without damage. This approach is revolutionary and offers new perspectives in the field of regenerative medicine.

Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSC) or Stromal Cells:
Used to create new body tissues like bones and cartilage, they could be key in treating a variety of health problems.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (IPSC):
Created in the laboratory from skin cells, they behave like embryonic stem cells and are promising for the development of various therapies.
The Issue of Donor-Recipient Compatibility
There are two main types of stem cell collections used in cell therapy:
- Autologous graft or autograft: The cells are harvested from the patient himself, ensuring perfect tolerance by his immune system.
- Allogeneic grafts: The stem cells are harvested from a donor different from the patient, which may raise issues of immune compatibility.
Mesenchymal and embryonic stem cells come into play here. Embryonic stem cells are generally low in immunogenicity and their use requires, in most cases, only temporary immunosuppressive treatment. Mesenchymal stem cells express HLA markers at a low level and secrete immunosuppressive factors, thus limiting immune reactions against the graft and making any exogenous immunosuppressive treatment superfluous.
WHAT CAN BE TREATED WITH STEM CELLS?
Many clinics and specialized hospitals now offer targeted treatments for specific diseases. These treatments range from autism to Crohn's disease, including multiple sclerosis. They also include advanced rejuvenating care.
Orthopedic Applications of Stem Cells
In the treatment of joint cartilage and osteoarthritis, stem cells - either autologous (from the patient) or from adipose tissue - show very promising results.
Use of Stem Cells in Regenerative Medicine
Stem cells play a crucial role in breast reconstruction after cancer, healing chronic wounds, and treating burns. In dermatology, the use of fibroblastic cells from the patient is effective for skin rejuvenation and acne scar treatment.
The competent authorities, notably the Turkish Ministry of Health, have already approved cellular treatments for the following pathologies:
- Covid-19 Pneumonia
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF)
- Chronic Pulmonary Obstruction
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- Diabetic Foot Injuries
- Peripheral Arterial Disease
- Spinal Cord Injury
- Cerebral Palsy (CP)
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
- Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE)
- Spinocerebellar Ataxia (SCA)
- Friedreich's Ataxia (FA)
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)
- Cystic Fibrosis (CF)
- Ischemic Heart Disease Treatment
- Autoimmune Encephalitis (AE)
- Limb Girdle of Miyoshi Myopathy
- Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy (LGMD)
- Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Stroke
- Congenital Progressive Myopathy
- Optic Atrophy
- Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP)
- Erectile Dysfunction
- Ovarian Failure
- Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis)
- Crohn's Disease
- Short Bowel Syndrome
Accessibility of Stem Cell Treatments
Thailand and Turkey stand out in the field of all types of stem cells. Esthetic Planet has established a strong presence there. Accessibility to embryonic stem cells (ESC) is the most important factor in selecting a destination for undergoing regenerative medicine treatment.
We collaborate with several leading clinics in Bangkok, Phuket, Istanbul, and Colombia. These establishments specialize in therapies based on all types of stem cells.
Furthermore, we work with several clinics offering anti-aging and orthopedic care, using stem cells, in Turkey and Thailand.
To receive a quote or more information about stem cell possibilities abroad, please fill out our quote request form. You will gain access to our clinic communication platform and discover the new world of regenerative medicine.
Image credit: https://www.biorbyt.com/
Image credit: https://www.novusbio.com/
Image credit: https://www.lifecell.in/